Thesis: ClimAIte Control – Stripp
-
Intro
-
Technical Aspects
Information
| Primary software used | Jupyter Notebook |
| Course | Thesis: ClimAIte Control – Stripp |
| Primary subject | AI & ML |
| Secondary subject | Machine Learning |
| Level | Beginner |
| Last updated | November 27, 2024 |
| Keywords |
Responsible
| Faculty |
Thesis: ClimAIte Control – Stripp 0/1
Thesis: ClimAIte Control – Stripp
Improving Building Operation Through AI by Sebastian Stripp
The thesis project uses a digital twin of a case study building to test how Q-Learning (a form of reinforcement learning) can be used to make building control decisions to reduce energy consumption.
To simulate building performance, it was necessary to create a digital twin. First, the building was modelled in Rhino and divided into two zones. The surfaces were then incorporated into Ladybug and Honeybee to provide the building energy model. This model was calibrated against historical data measured on-site and ASHRAE guidelines were used to validate the digital twin.
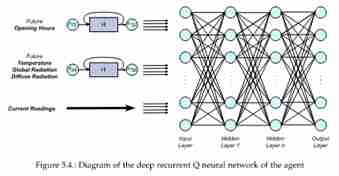
In order to investigate saving energy while maintaining comfort, Reinforcement Learning agents were designed, coded, and tested together with 9 building variations of the digital twin. The main method of Reinforcement Learning used is Deep Q-Learning (DQN) which approximates the reward of different actions and chooses the one with the highest reward. To take the action with the highest reward, a fully-connected simple Neural Network (NN) is trained to understand the relationships between actions and expected rewards. Additionally, at each step the time-based data from the weather forecast are processed using a recurrent Neural Networks (RNN). Combining these two methods results in a Deep Recurrent Q-Learning (DRQN) model.
LIMITATIONS: Only a few different RL algorithm types were evaluated in a small number of combinations.
APA: Stripp, S. (2023). ClimAIte Control [Master thesis, TU Delft]. https://repository.tudelft.nl/record/uuid:963a53d8-2dc0-4d2a-988d-612c72856e0d
Here you can find the repository of the master thesis ClimAIte Control | TU Delft Repository
Project Information
- Title: ClimAIte Control
- Author(s): Sebastian Stripp
- Year: 2023
- Link: https://repository.tudelft.nl/record/uuid:963a53d8-2dc0-4d2a-988d-612c72856e0d
- Type: Master thesis, Building Technology
- ML tags: Q-Learning, Neural Networks, Reinforcement Learning
- Topic tags: Building Energy Control, Digital Twins
Thesis: ClimAIte Control – Stripp 1/1
Technical Aspectslink copied
Software & Plug-ins Used
- SketchUp and Rhino for 3D Modelling
- Grasshopper with plug-ins Honeybee and Ladybug for Visual Programming
- Energy Plus for Energy Modelling
- Python using Pytorch for Deep Q-Learning
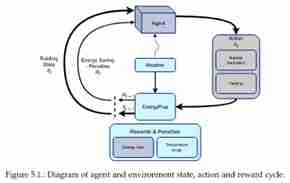
The thesis investigates if it is possible to reduce the energy use of existing buildings by optimizing their operation through deep reinforcement learning (DRL). A reinforcement learning model is trained by having an agent take actions in a simulated environment (digital twin) with select decisions (opening ventilation louvres, setting the thermostat), weather forecast information and building use information (if the building is occupied or not). The goal of the model is to reduce energy usage and improve occupant comfort.
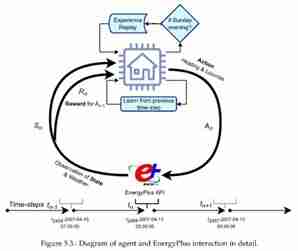
This is a more detailed diagram of the interaction between the agent and EnergyPlus.
Write your feedback.
Write your feedback on "Thesis: ClimAIte Control – Stripp"".
If you're providing a specific feedback to a part of the chapter, mention which part (text, image, or video) that you have specific feedback for."Thank your for your feedback.
Your feedback has been submitted successfully and is now awaiting review. We appreciate your input and will ensure it aligns with our guidelines before it’s published.
